As its based on the GCC compiler, it is prepared for both ANSI with CCI compliance. Ill keep with the basics out of type defs.
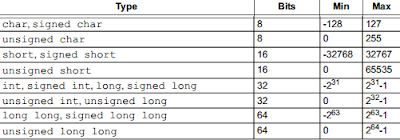
The ANSI C Standard does indicate minimum requirements for these
types, as specified in
* For more info on compiler compliance check the XC32 Compiler User guide in chapter “2.4.6 Sizes of Type
From researching the include files, one can get this info :
/* 7.18.1.1 Exact-width integer types */
typedef __signed char __int8_t;
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
typedef short int __int16_t;
typedef unsigned short int __uint16_t;
typedef int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t;
#ifdef __COMPILER_INT64__
typedef __COMPILER_INT64__ __int64_t;
typedef __COMPILER_UINT64__ __uint64_t;
#elif defined(_LP64)
typedef long int __int64_t;
typedef unsigned long int __uint64_t;
#else
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef long long int __int64_t;
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef unsigned long long int __uint64_t;
#endif
#define __BIT_TYPES_DEFINED__
Which gives us :
// MPLAB C32 range of Signed values
char c; // -128 to 127
short s; // -32,768 to 32,767
int i; // -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
long l; // -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
Of course, we also have the unsigned attribute:
// MPLAB C32 range of Unsigned values
unsigned char c; // 0 to 255
unsigned short s; // 0 to 65,535
unsigned int i; // 0 to 4,294,967,295
unsigned long l; // 0 to 4,294,967,295
For int, 4 bytes in the physical RAM is used.
So, if we do not have to use int and long, we should use char.
To hold one char variable, C32 compiler will use only 8 bits.
Another possibility is short type, which will use 16 bits to hold one short variable
PIC32‘s ALU is performing all arithmetic operations in the same number of cycles for 32-bit, 16-bit or 8-bit integers, which turns the variable long into just a synonym of the basic integer type int.
It is ok from performance point of view, but it comes with a price.
The only limiting factor, preventing us from always using 32-bit integers , is the consideration of the internal resources , and in this case the RAM memory
* keep the size of your variables to the minimum necessary; operating on bytes versus word can make a big difference in terms of code compactness/efficiency.
If really a large range of values is needed, we can use 64-bit types
// C32 range of 64-bit type values
long long l; // ranges from -2 to the power of 63 to +2 to the power of 63-1
unsigned long long l; // ranges from 0 to +2 to the power of 64
// C32 range of Floating point type values
float f; // 32-bit floating point
double d; // 64-bit floating point
long double d; // 64-bit floating point, synonym of double
The long long integer type offers 64-bit support and requires 8 bytes of memory; So, we can expect a small performance decrease for using long long integers.
Ill leave several excerpts from the header files...
/* 7.18.1.1 Exact-width integer types */
typedef __signed char __int8_t;
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
typedef short int __int16_t;
typedef unsigned short int __uint16_t;
typedef int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t;
#ifdef __COMPILER_INT64__
typedef __COMPILER_INT64__ __int64_t;
typedef __COMPILER_UINT64__ __uint64_t;
#elif defined(_LP64)
typedef long int __int64_t;
typedef unsigned long int __uint64_t;
#else
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef long long int __int64_t;
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef unsigned long long int __uint64_t;
#endif
#define __BIT_TYPES_DEFINED__
/* 7.18.1.4 Integer types capable of holding object pointers */
#ifdef _LP64
typedef long int __intptr_t;
typedef unsigned long int __uintptr_t;
#else
typedef int __intptr_t;
typedef unsigned int __uintptr_t;
#endif
#endif /* !_MIPS_INT_TYPES_H_ */
Also :
* 7.18.1.2 Minimum-width integer types */__extension__
typedef __signed char int_least8_t;
typedef unsigned char uint_least8_t;
typedef short int int_least16_t;
typedef unsigned short int uint_least16_t;
typedef int int_least24_t;
typedef unsigned int uint_least24_t;
typedef int int_least32_t;
typedef unsigned int uint_least32_t;
#ifdef __COMPILER_INT64__
typedef __COMPILER_INT64__ int_least64_t;
typedef __COMPILER_UINT64__ uint_least64_t;
#elif defined(_LP64)
typedef long int int_least64_t;
typedef unsigned long int uint_least64_t;
#else
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef long long int int_least64_t;
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef unsigned long long int uint_least64_t;
#endif
/* 7.18.1.3 Fastest minimum-width integer types */
typedef int int_fast8_t;
typedef unsigned int uint_fast8_t;
typedef int int_fast16_t;
typedef unsigned int uint_fast16_t;
typedef int int_fast24_t;
typedef unsigned int uint_fast24_t;
typedef int int_fast32_t;
typedef unsigned int uint_fast32_t;
#ifdef __COMPILER_INT64__
typedef __COMPILER_INT64__ int_fast64_t;
typedef __COMPILER_UINT64__ uint_fast64_t;
#elif defined(_LP64)
typedef long int int_fast64_t;
typedef unsigned long int uint_fast64_t;
#else
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef long long int int_fast64_t;
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef unsigned long long int uint_fast64_t;
#endif
/* 7.18.1.5 Greatest-width integer types */
#ifdef __COMPILER_INT64__
typedef __COMPILER_INT64__ intmax_t;
typedef unsigned __COMPILER_INT64__ uintmax_t;
#elif defined(_LP64)
typedef long int intmax_t;
typedef unsigned long int uintmax_t;
#else
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef long long int intmax_t;
/* LONGLONG */
__extension__
typedef unsigned long long int uintmax_t;
#endif
#endif /* !_MIPS_INT_MWGWTYPES_H_ */
Regarding the limits of each type def...
/* $NetBSD: int_limits.h,v 1.3 2002/11/03 19:55:23 thorpej Exp $ */
/*-
* Copyright (c) 2001 The NetBSD Foundation, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*/
...
/*
* 7.18.2 Limits of specified-width integer types
*/
/* 7.18.2.1 Limits of exact-width integer types */
/* minimum values of exact-width signed integer types */
#define INT8_MIN (-0x7f-1) /* int8_t */
#define INT16_MIN (-0x7fff-1) /* int16_t */
#define INT32_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* int32_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define INT64_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffL-1) /* int64_t */
#else
#define INT64_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffLL-1) /* int64_t */
#endif
/* maximum values of exact-width signed integer types */
#define INT8_MAX 0x7f /* int8_t */
#define INT16_MAX 0x7fff /* int16_t */
#define INT32_MAX 0x7fffffff /* int32_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define INT64_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffL /* int64_t */
#else
#define INT64_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffLL /* int64_t */
#endif
/* maximum values of exact-width unsigned integer types */
#define UINT8_MAX 0xffU /* uint8_t */
#define UINT16_MAX 0xffffU /* uint16_t */
#define UINT32_MAX 0xffffffffU /* uint32_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define UINT64_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffUL /* uint64_t */
#else
#define UINT64_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffULL /* uint64_t */
#endif
/* 7.18.2.2 Limits of minimum-width integer types */
/* minimum values of minimum-width signed integer types */
#define INT_LEAST8_MIN (-0x7f-1) /* int_least8_t */
#define INT_LEAST16_MIN (-0x7fff-1) /* int_least16_t */
#define INT_LEAST24_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* int_least24_t */
#define INT_LEAST32_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* int_least32_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define INT_LEAST64_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffL-1) /* int_least64_t */
#else
#define INT_LEAST64_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffLL-1) /* int_least64_t */
#endif
/* maximum values of minimum-width signed integer types */
#define INT_LEAST8_MAX 0x7f /* int_least8_t */
#define INT_LEAST16_MAX 0x7fff /* int_least16_t */
#define INT_LEAST24_MAX 0x7fffffff /* int_least24_t */
#define INT_LEAST32_MAX 0x7fffffff /* int_least32_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define INT_LEAST64_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffL /* int_least64_t */
#else
#define INT_LEAST64_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffLL /* int_least64_t */
#endif
/* maximum values of minimum-width unsigned integer types */
#define UINT_LEAST8_MAX 0xffU /* uint_least8_t */
#define UINT_LEAST16_MAX 0xffffU /* uint_least16_t */
#define UINT_LEAST24_MAX 0xffffffffU /* uint_least24_t */
#define UINT_LEAST32_MAX 0xffffffffU /* uint_least32_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define UINT_LEAST64_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffUL /* uint_least64_t */
#else
#define UINT_LEAST64_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffULL /* uint_least64_t */
#endif
/* 7.18.2.3 Limits of fastest minimum-width integer types */
/* minimum values of fastest minimum-width signed integer types */
#define INT_FAST8_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* int_fast8_t */
#define INT_FAST16_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* int_fast16_t */
#define INT_FAST24_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* int_fast24_t */
#define INT_FAST32_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* int_fast32_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define INT_FAST64_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffL-1) /* int_fast64_t */
#else
#define INT_FAST64_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffLL-1) /* int_fast64_t */
#endif
/* maximum values of fastest minimum-width signed integer types */
#define INT_FAST8_MAX 0x7fffffff /* int_fast8_t */
#define INT_FAST16_MAX 0x7fffffff /* int_fast16_t */
#define INT_FAST24_MAX 0x7fffffff /* int_fast24_t */
#define INT_FAST32_MAX 0x7fffffff /* int_fast32_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define INT_FAST64_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffL /* int_fast64_t */
#else
#define INT_FAST64_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffLL /* int_fast64_t */
#endif
/* maximum values of fastest minimum-width unsigned integer types */
#define UINT_FAST8_MAX 0xffffffffU /* uint_fast8_t */
#define UINT_FAST16_MAX 0xffffffffU /* uint_fast16_t */
#define UINT_FAST24_MAX 0xffffffffU /* uint_fast24_t */
#define UINT_FAST32_MAX 0xffffffffU /* uint_fast32_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define UINT_FAST64_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffUL /* uint_fast64_t */
#else
#define UINT_FAST64_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffULL /* uint_fast64_t */
#endif
/* 7.18.2.4 Limits of integer types capable of holding object pointers */
#ifdef _LP64
#define INTPTR_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffL-1) /* intptr_t */
#define INTPTR_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffL /* intptr_t */
#define UINTPTR_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffUL /* uintptr_t */
#else
#define INTPTR_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* intptr_t */
#define INTPTR_MAX 0x7fffffff /* intptr_t */
#define UINTPTR_MAX 0xffffffffU /* uintptr_t */
#endif
/* 7.18.2.5 Limits of greatest-width integer types */
#ifdef _LP64
#define INTMAX_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffL-1) /* intmax_t */
#define INTMAX_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffL /* intmax_t */
#define UINTMAX_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffUL /* uintmax_t */
#else
#define INTMAX_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffLL-1) /* intmax_t */
#define INTMAX_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffLL /* intmax_t */
#define UINTMAX_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffULL /* uintmax_t */
#endif
/*
* 7.18.3 Limits of other integer types
*/
/* limits of ptrdiff_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define PTRDIFF_MIN (-0x7fffffffffffffffL-1) /* ptrdiff_t */
#define PTRDIFF_MAX 0x7fffffffffffffffL /* ptrdiff_t */
#else
#define PTRDIFF_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* ptrdiff_t */
#define PTRDIFF_MAX 0x7fffffff /* ptrdiff_t */
#endif
/* limits of sig_atomic_t */
#define SIG_ATOMIC_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* sig_atomic_t */
#define SIG_ATOMIC_MAX 0x7fffffff /* sig_atomic_t */
/* limit of size_t */
#ifdef _LP64
#define SIZE_MAX 0xffffffffffffffffUL /* size_t */
#else
#define SIZE_MAX 0xffffffffU /* size_t */
#endif
#ifndef WCHAR_MIN /* also possibly defined in
/* limits of wchar_t */
#define WCHAR_MIN 0 /* wchar_t */
#define WCHAR_MAX 0xffff /* wchar_t */
/* limits of wint_t */
#define WINT_MIN (-0x7fffffff-1) /* wint_t */
#define WINT_MAX 0x7fffffff /* wint_t */
#endif
#endif /* !_MIPS_INT_LIMITS_H_ */
(1): http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/51686F.pdf
(2): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6FNKJSWuaJE
No comments:
Post a Comment
Feel free to contact me with any suggestions, doubts or requests.
Bless